Rising global temperatures are directly linked to increased concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere These gases warm the Earth's surface by trapping heat Most of the increase in their atmospheric levels comes from human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuelsA greenhouse gas (GHG) is any gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation in the thermal infrared range These are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect, which results in increased temperatures on Earth The greenhouse effect occurs as the gases reach Earth's surfaceIn turn, these changes might be expected to alter the production and consumption of the important greenhouse gases nitrous oxide (N(2)O) and methane (CH(4)) (refs 2, 3) However, studies on fluxes of N(2)O and CH(4) from soil under increased atmospheric CO(2) have not been quantitatively synthesized
Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency
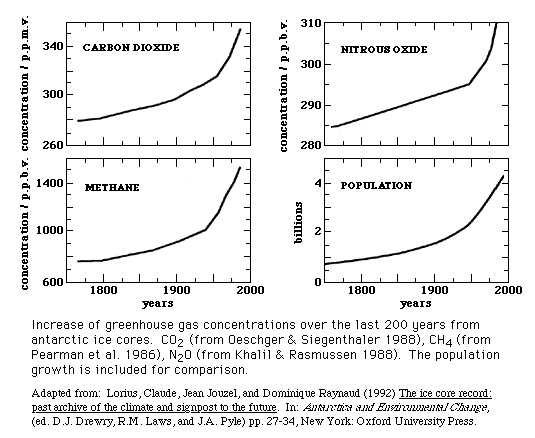
Increase amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
Increase amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere- The graphs show monthly mean carbon dioxide measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii The carbon dioxide data on Mauna Loa constitute the longest record of direct measurements of CO 2 in the atmosphere They were started by C David Keeling of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in March of 1958 at a facility of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, nitrous oxides, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) On Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouse Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric CO 2 This happens because the coal or oil




Warming Influence Of Greenhouse Gases Continues To Rise Noaa Finds Welcome To Noaa Research
The increased greenhouse effect is causing changes in our planet that can affect our lives The major Greenhouse Gas, carbon dioxide, emitted naturally and by the burning of fossil fuels, stays in the atmosphere a long time Its warming effect occurs even when the sky is clear and dry Climate scientists are so concerned about carbon dioxide The greenhouse gases that humans do emit directly in significant quantities are Carbon dioxide (CO2) Accounts for around threequarters of the warming impact of current human greenhousegasHuman activity, primarily the burning of fossil fuels during the past 250 years, has caused wellquantified increases in the concentrations of GHGs in the atmosphere (Figure ATM1)This has resulted in significant increases in positive radiative forcing, which has a warming effect on the climate (Figure ATM2)The CSIRO global GHGobserving network recorded a global CO 2 atmospheric
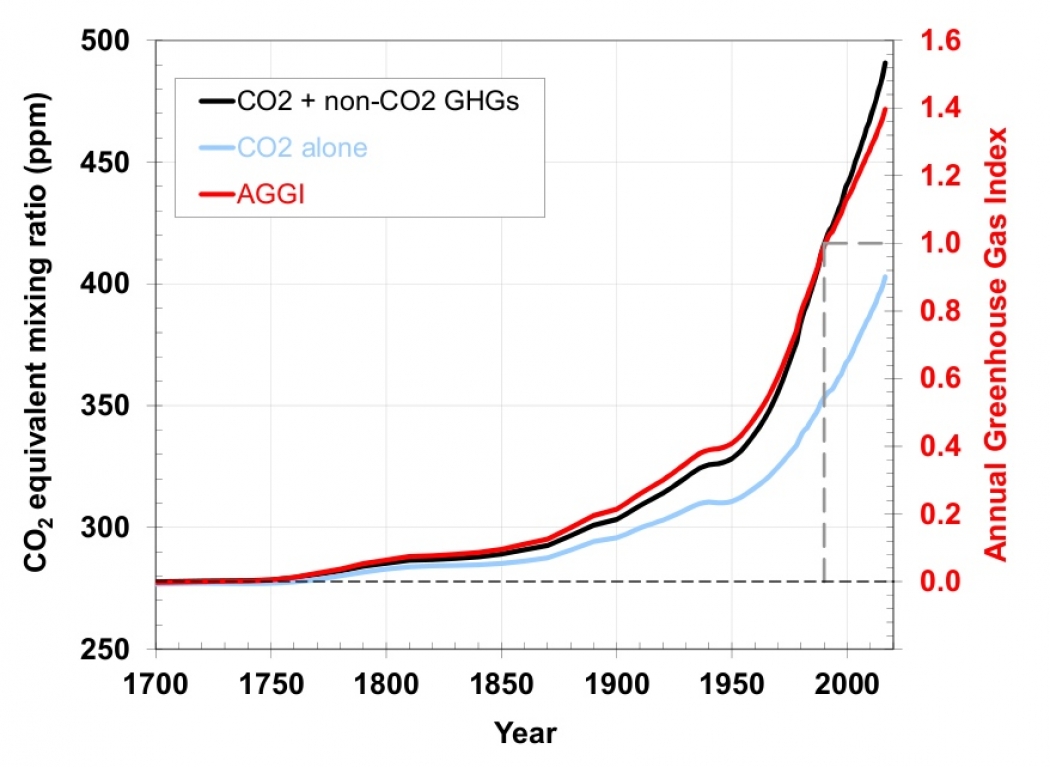
It took ~240 years for the AGGI to go from 0 to 1, ie, to reach 100%, and 30 years for it to increase by another 47% In terms of CO 2 equivalents, the atmosphere in contained 504 ppm, of which 412 is CO 2 alone The rest comes from other gasesGreenhouse gases Global average concentrations of all the major longlived greenhouse gases continue to rise in the atmosphere, with the global annual mean carbon dioxide concentration reaching 410 ppm and CO 2 equivalent reaching 508 ppm in 19; Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide is the main longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere related to human activities Its concentration reached new highs in 18 of 4078 ppm, or 147% of preindustrial level in 1750 The increase in CO2 from 17 to 18 was above the average growth rate over the last decade The growth rate of CO2 averaged over
In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time Rising temperatures may produce changes in precipitation patterns, storm severity, and sea level Collectively, this is commonly referred to as climate change Last Updated on Sat, Greenhouse Gases Climate change is being caused by a combination of factors, but the most important is the increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, and especially carbon dioxide Most of this extra carbon dioxide is being released by burning carbonrich fuels By increasing the heat in the atmosphere, greenhouse gases are responsible for the greenhouse effect, which ultimately leads to global warming




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases
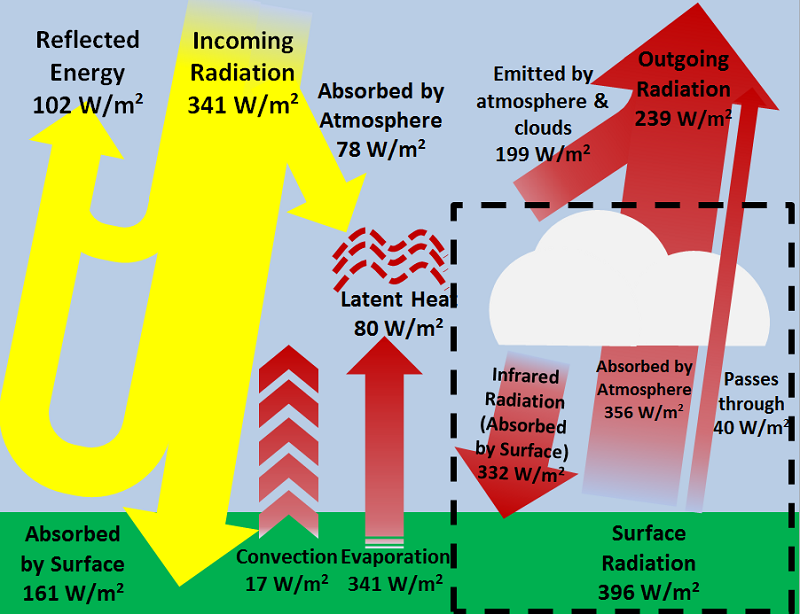



The Greenhouse Effect And Earth S Energy Budget Energy Education
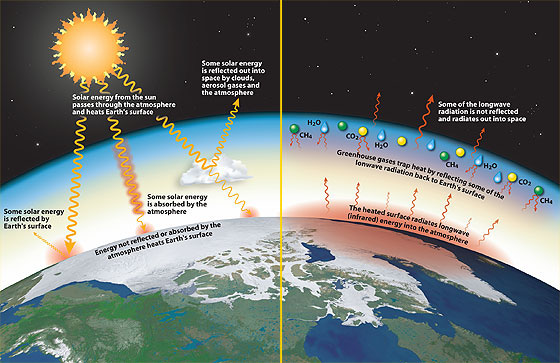
Greenhouse gases absorb and reemit radiant heat energy from the sun They hold onto that heat energy for a much longer period of time than do other atmospheric gases Water vapor is the Earth's most important natural Today's atmosphere absorbs more than 3 watts of incoming solar energy over each square meter of Earth's surface According to NOAA's 19 Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (right axis), the combined heating influence of all major greenhouse gases has increased by 45% relative to 1990 Graph by NOAA Climategov based on data from NOAA ESRLGreenhouse gases are gases in an atmosphere that absorb and emit radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect Common greenhouse



Greenhouse Gases



Cilab Greenhouse Gases Effect On Global Warming
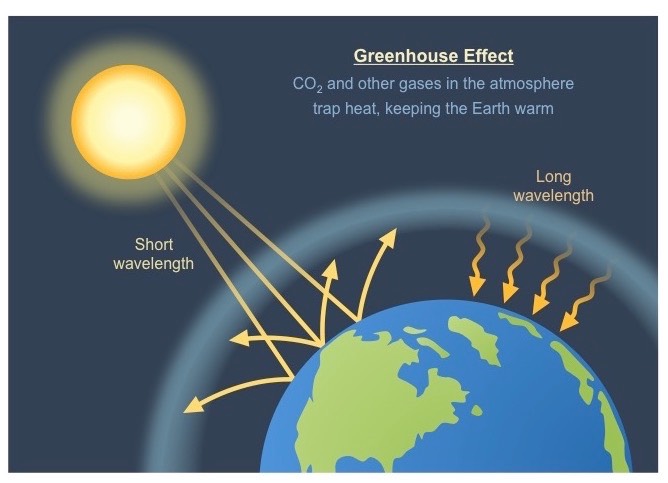
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, including water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, absorb heat energy and emit it in all directions (including downwards), keeping Earth's surface and lower atmosphere warm Adding more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere enhances the effect, making Earth's surface and lower atmosphere Composition of Atmosphere – Gases in the Atmosphere The atmospheric composition of gas on Earth is largely conducted by the byproducts of the life that it nurtures Dry air from earth's atmosphere contains 0038% of carbon dioxide, 95% of oxygen, 7808% of nitrogen and 093% of argonMethane (CH 4) is the second most abundant greenhouse gas Atmospheric concentrations have increased by about 150%, and methane is more abundant now than at any time in the last 800,000 years Globally, the leading sources of humaninfluenced methane emissions are from agriculture – primarily from livestock and rice production



The Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence ofMain Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedBuildup of greenhouse gases One problem that was brought about by human action and is definitely affecting the hydrosphere globally is that of the greenhouse gases (so called because of their heattrapping "greenhouse" properties) emitted to the atmosphereOf the greenhouse gases released by anthropogenic activities, carbon dioxide has received much attention




25 Wonderful Ways To Reduce Greenhouse Gases Conserve Energy Future




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Since the Industrial Revolution of the late 1700s and early 1800s, people have been releasing larger quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere That amount has skyrocketed in the past century Greenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04 Emissions of CO 2, rose by about 80 percent during that time These five primary greenhouse gases account for about 96 percent of the increased climate warming influence since 1750 The index tracks five primary gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and two chlorofluorocarbons that were banned by the Montreal Protocol because they damage Earth's protective ozone layer
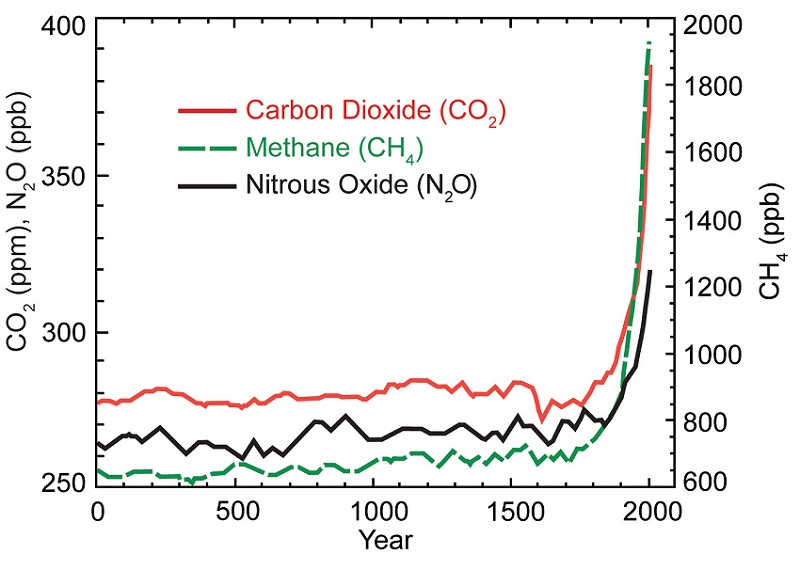



Causes Of Climate Change Climate Change Science Us Epa




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
The rate of CO 2 accumulation in the atmosphere has increased with every passing decade since atmospheric measurementsHuman Activity and the Greenhouse Effect ID506 How do increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere lead to warmer temperatures?The growing concentrations of humangenerated GHGs have resulted in an increased absorption, largely in the lower atmosphere, of the heat radiated from Earth's surface, causing an increase in the global (land and ocean) mean surface temperature of 085 ± 0 °C from 10 to 12 (Stocker et al 13a)—a longterm average increase of 006–007 °C per decade However, this rise did not occur evenly across the century—for example, average global temperatures did not increase
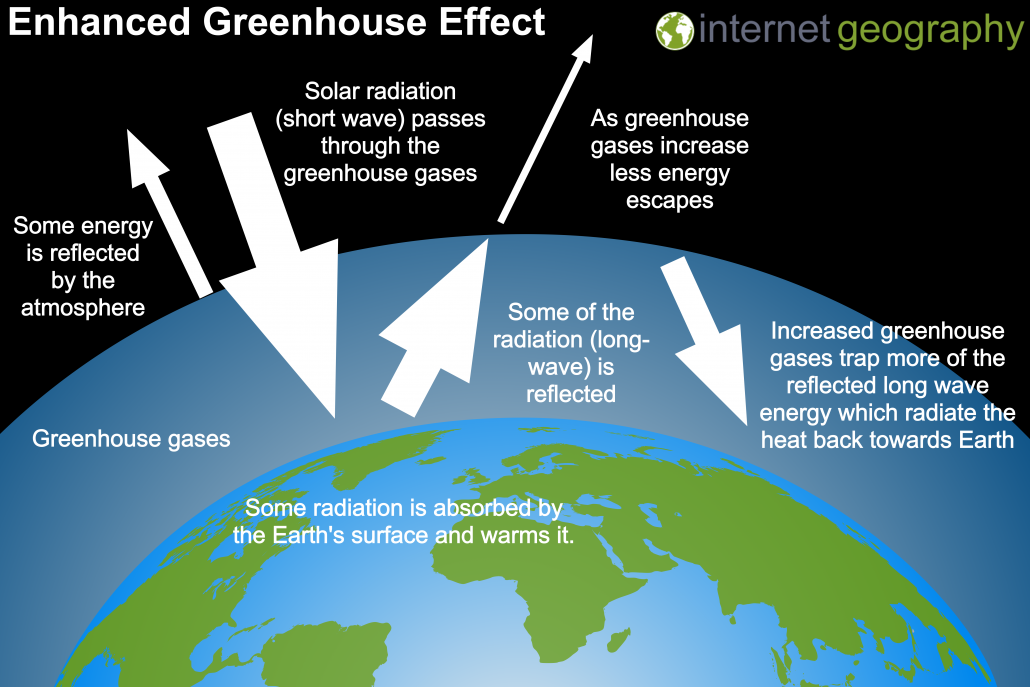



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today
Greenhouse Gases, Carbon Dioxide And Methane, Rise Sharply In 07 Last year alone global levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide, the primary driver of global climate change, increased by 06 Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO 2) This happens because the coal or oil burning process combines carbon with oxygen in the air to make CO 24 реда An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate
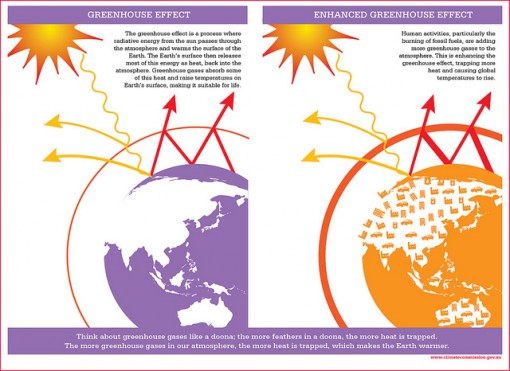



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
Carbon dioxide controls the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere and thus the size of the greenhouse effect Rising carbon dioxide concentrations are already causing the planet to heat up At the same time that greenhouse gases have been increasing, average global temperatures have risen 08 degrees Celsius (14 degrees Fahrenheit) since 10 Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide is the main longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere related to human activities Its concentration reached new highs in 18 of 4078 ppm, or 147 percent of preThe early atmosphere was mainly carbon dioxide and water vapour Human activities are releasing greenhouse gases which are causing global warming, and other atmospheric pollutants




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
The effect of greenhouse gases There are five gases of human origin that contribute most – together up to 95% of the total – to the increase in global warming Here you will discover the source of their emission, the time they spend in the atmosphere and what percentage they contribute to the greenhouse effectLarger emissions of greenhouse gases lead to higher concentrations in the atmosphere Greenhouse gas concentrations are measured in parts per million, parts per billion, and even parts per trillion One part per million is equivalent to one drop of water diluted into about 13 gallons of liquid (roughly the fuel tank of a compact car)The enhanced greenhouse effect is generally what is being talked about when people refer to the greenhouse effect and climate change This effect refers to the increased heating of the Earth's surface as a result of a higher amount of greenhouse gases being released into the atmosphere from human activities




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record World Meteorological Organization




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious
Total radiative forcing of all longlived greenhouse gases – the balance between radiation coming into the atmosphere and radiation going out – increased by 1% in 09 and rose by 275% from Unfortunately, the increased carbon dioxide in the ocean replaces water and makes it more acidic This is called ocean acidification More acidic water is harmful to some marine life, such as shellfish and coral Warm oceans – from the vast majority of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere – are also harmful to these organismsHowever, the vast majority of scientists do believe that humans are responsible for the increase in greenhouse gases and therefore global warming This is because the majority of evidence in




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gases
The AGGI in was 147, which means that we've turned up the warming influence from greenhouse gases by 47% since 1990; Major greenhouse gases and sources Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) Carbon dioxide is the primary greenhouse gas, responsible for about threequarters of emissions It can linger in the atmosphere forAdding more of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide increases this height The temperature at this height adjusts to radiate to space as much energy as is received from the Sun, and, the physics of the atmosphere cause the temperature to increase downward (squeezing air under higher pressure does work on the air that increases its




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
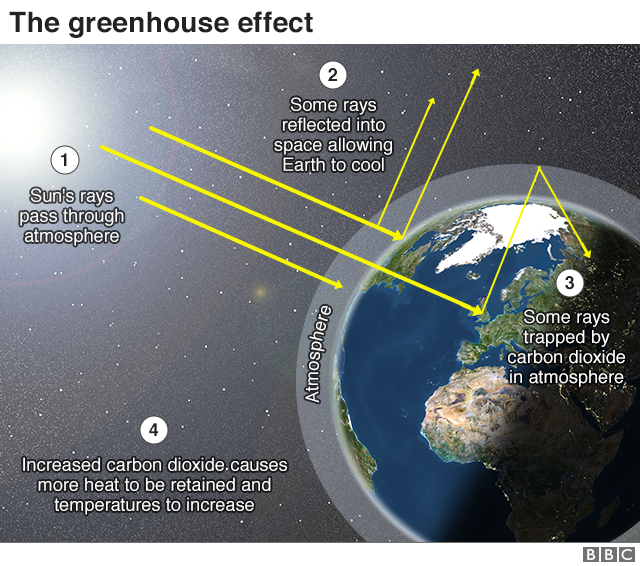



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News
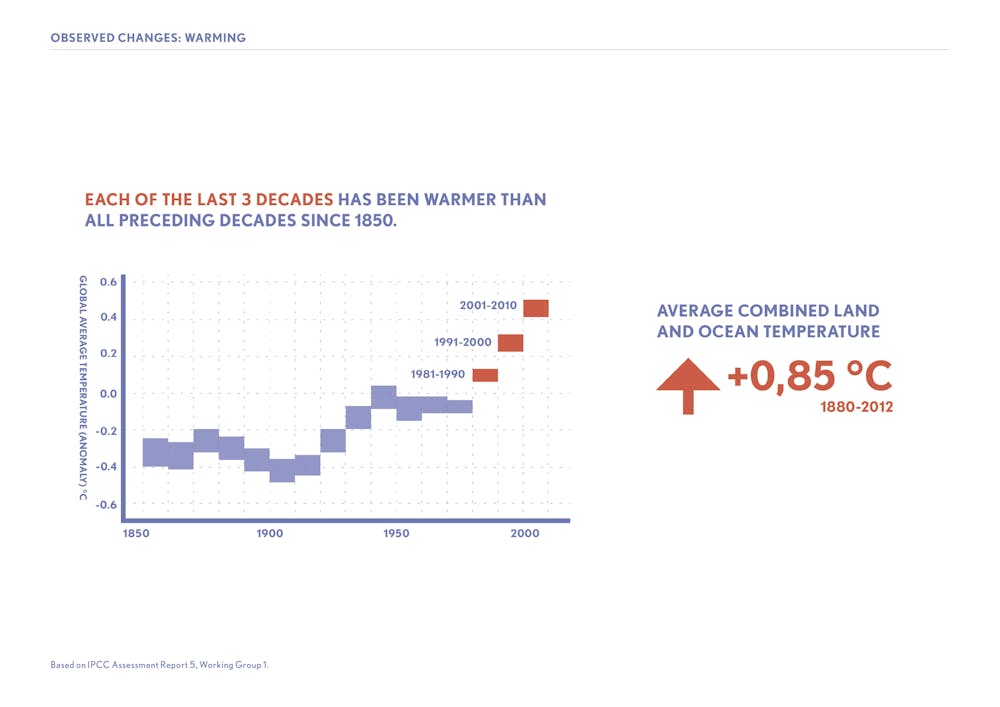



What Would Happen To The Climate If We Stopped Emitting Greenhouse Gases Today



Humans And The Greenhouse Effect Climate Institute




Global Warming




The Greenhouse Effect Is A Natural Process Where Heat Chegg Com




Greenhouse Effect And Historical Emissions



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization
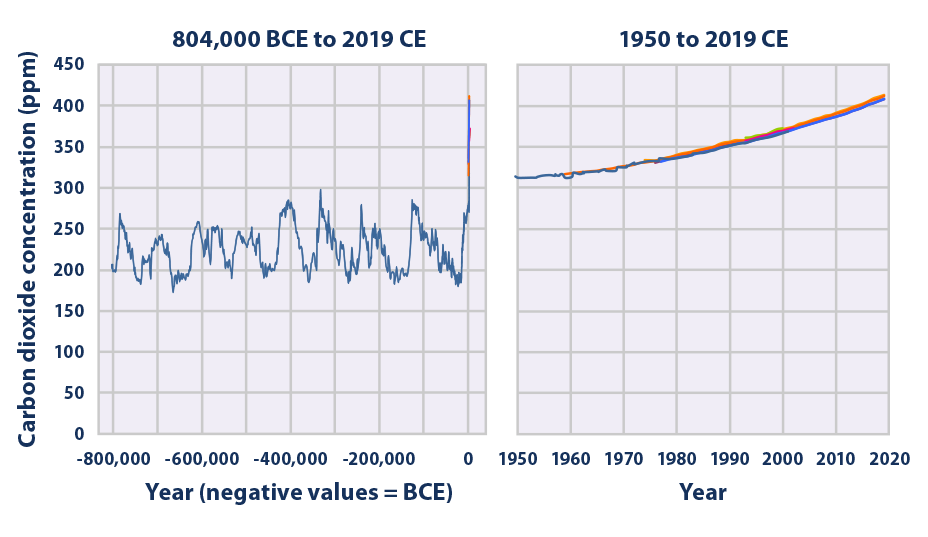



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Atmo336 Fall




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record World Meteorological Organization




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems



V1003 Science And Society Sources And Impacts Of Greenhouse Gases



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Increased Greenhouse Effect Due To Increase In Greenhouse Gases Leading Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Warming Influence Of Greenhouse Gases Continues To Rise Noaa Finds Welcome To Noaa Research




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering



Q Tbn And9gcqob5akx 2xithdb3seiv5jyef5ryrbg3xvzguy4p57lypo5m0p Usqp Cau
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Effect Department Of Agriculture Water And The Environment



Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



1




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central



Too Much Of A Good Thing




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




What Are Climate Change And Global Warming The Planet App



Greenhouse Gas Basics 148 Msu Extension



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Space



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja



Greenhouse Gases Is It Just A Lot Of Hot Air Thrive Blog




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Effects Of Increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions What S Your Impact




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



The Greenhouse Effect
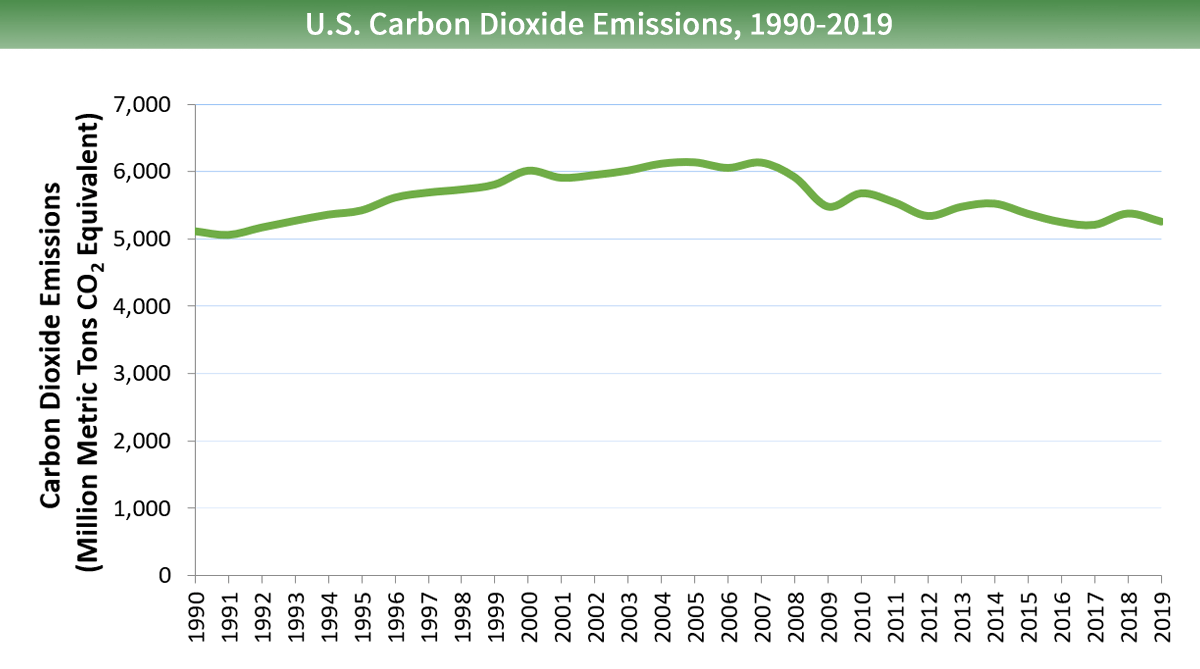



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature



Greenhouse Effect Body Used Water Process Earth Plants Form Energy Gas




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



Greenhouse Gases
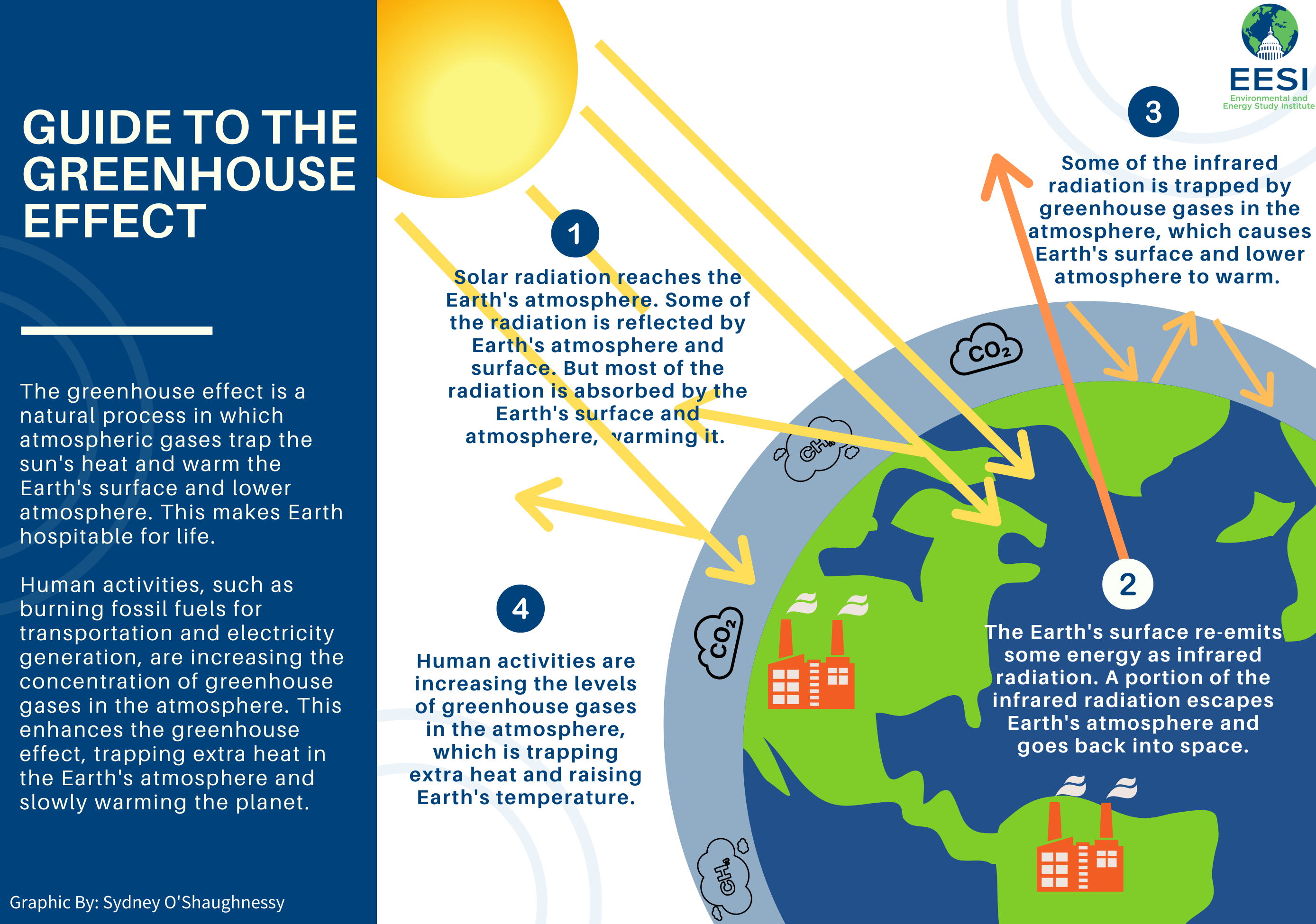



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi
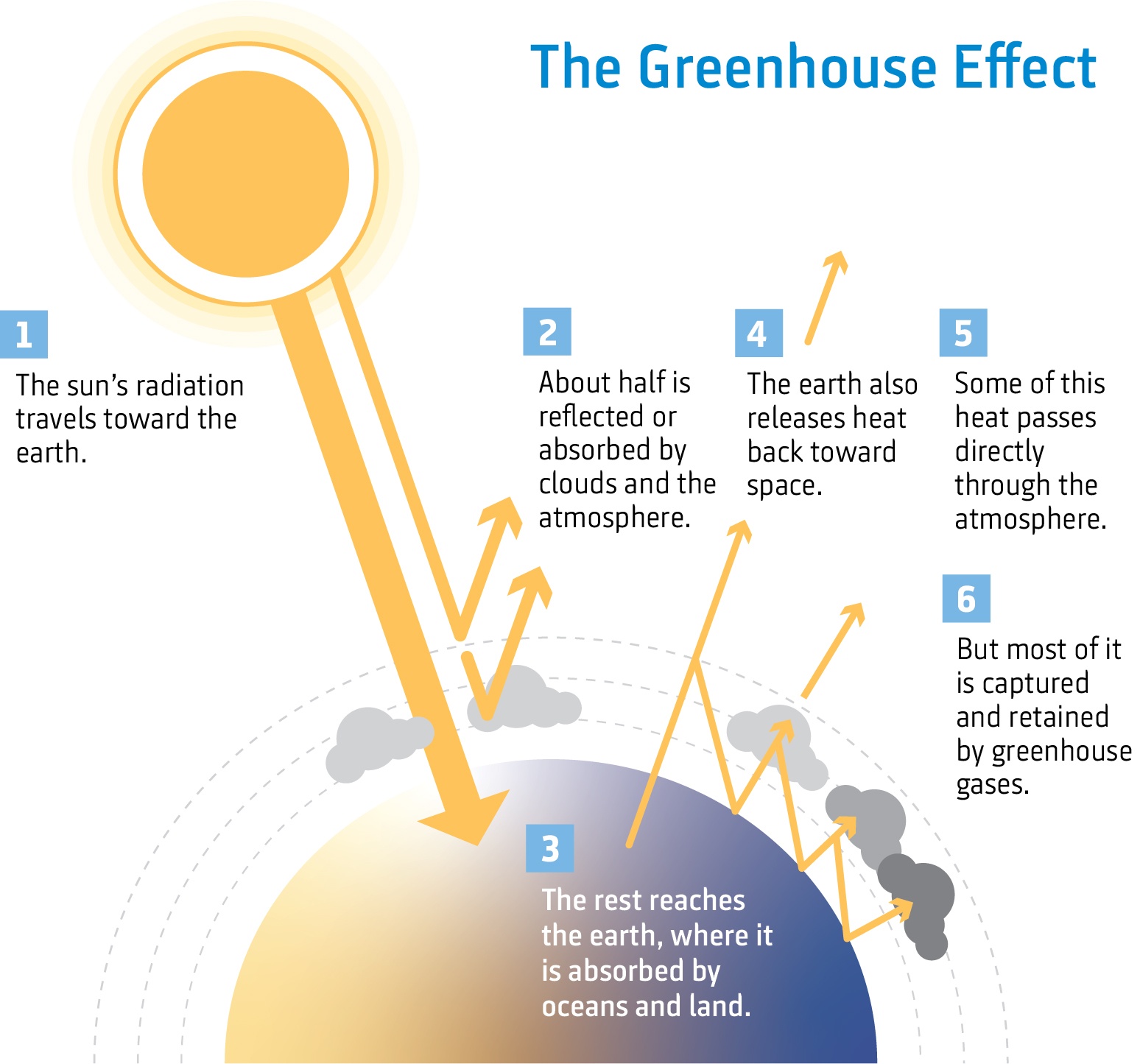



Climate Change The Science Niwa




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
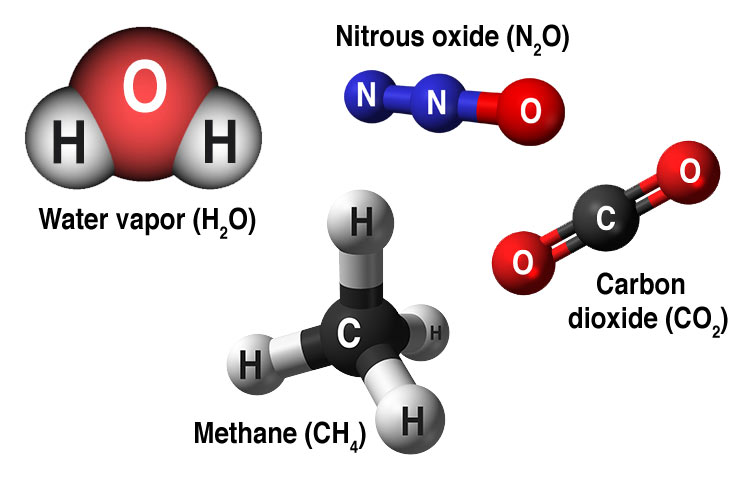



Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research



The Greenhouse Effect
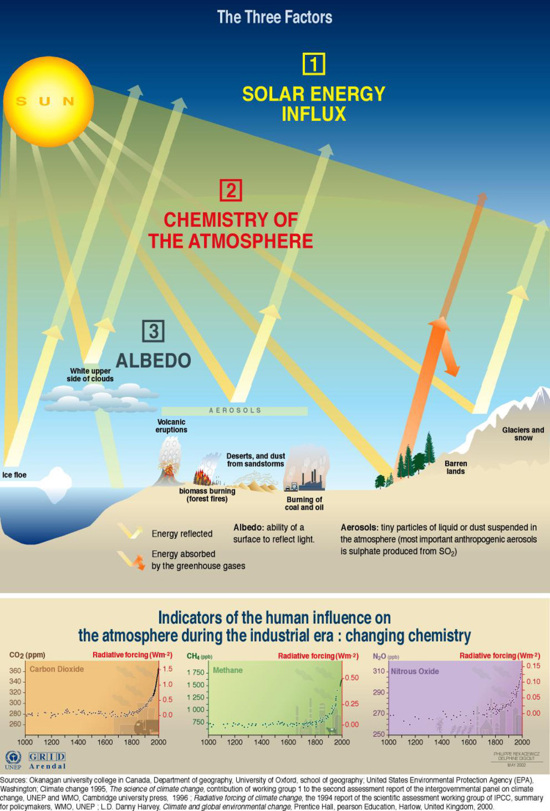



Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
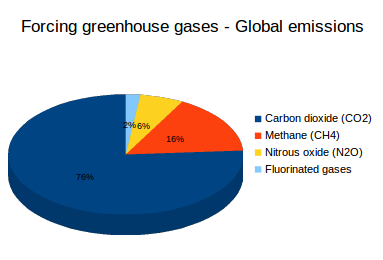



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact



If Carbon Dioxide Increases The Greenhouse Effect Are There Any Gases That Would Reduce Or Counteract This Effect Quora



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia



1




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



1
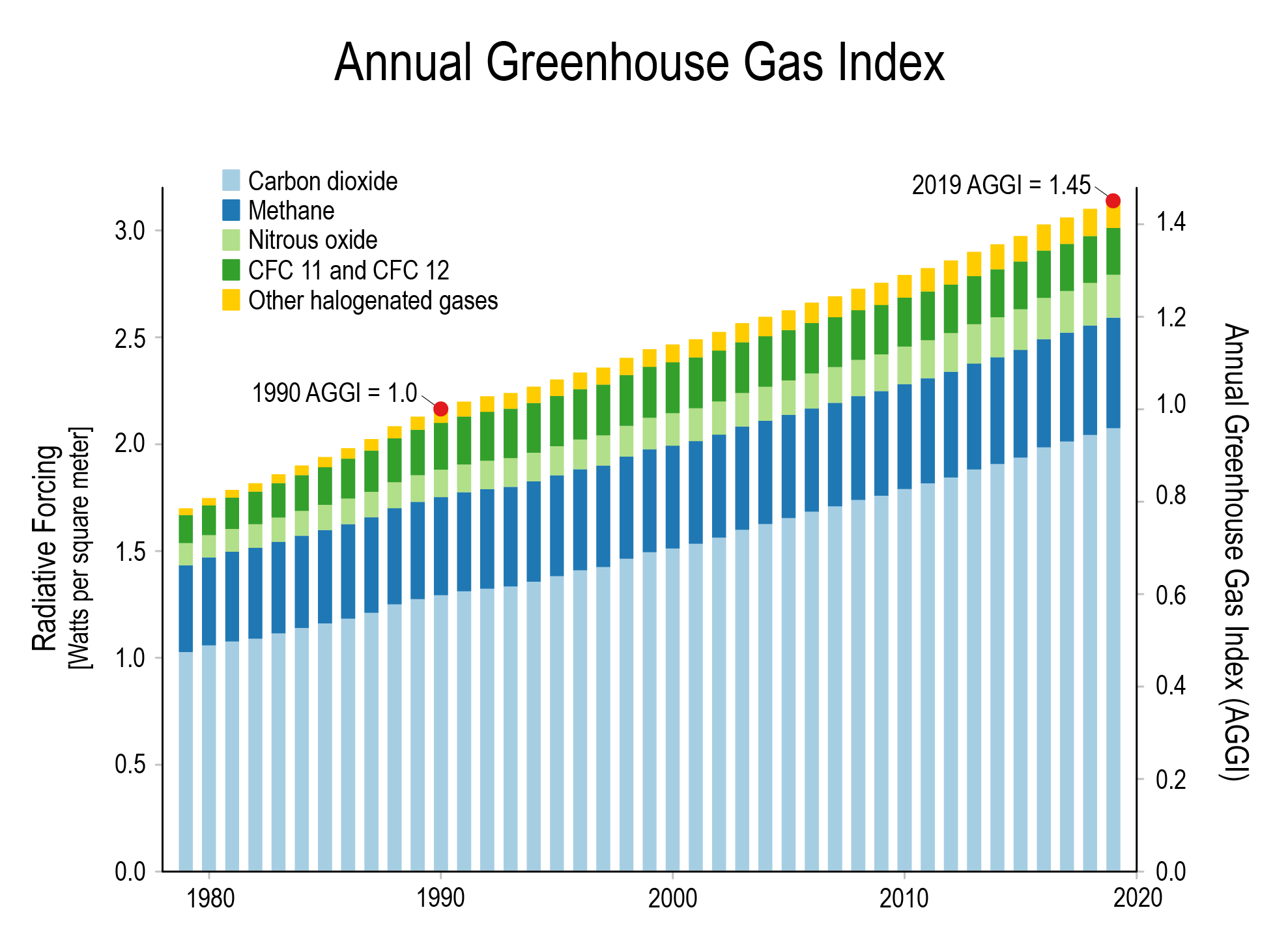



Climate Change International Ccs Knowledge Centre



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet


