Net emissions of greenhouse gases of anthropogenic actionspng 927 × 716; Mitigation – reducing climate change – involves reducing the flow of heattrapping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, either by reducing sources of these gases (for example, the burning of fossil fuels for electricity, heat or transport) or enhancing the "sinks" that accumulate and store these gases (such as the oceans, forests and soil)On Earth, natural and humancaused processes affect the amount of energy received as well as emitted back to space;

Mr Gruszka S Earth Science Giftionary Day 036 Giftionary Mechanisms Of The Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse gases gif
Greenhouse gases gif-Breakdown of Edinburgh's greenhouse gas emissions The City of Edinburgh Council 479 views July 1 028 Edinburgh's Emissions breakdown The City of Edinburgh Council 716 views June 27 022 Net Zero Explainer The City of Edinburgh Council Videos Vaccination gif Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does not




File Greenhouse Gases In Global Warming Effect Gif Wikimedia Commons
Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6"Greenhouse gases are the gases that absorb the infrared radiations and create a greenhouse effect For eg, carbondioxide and chlorofluorocarbons" Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation, etcFileEPA logosvg Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file 800 × 246 pixels Other resolutions 3 × 98 pixels 640 × 197 pixels 1,024 × 315 pixels 1,280 × 393 pixels 1,006 × 309 pixels This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons Information from its description page there is shown below Commons is a freely licensed media file
The same greenhouse gasses that pollute the Earth would be key to warming Mars The following options are among the methods being considered ForMolecules vibrate Molecules that have just two atoms vibrate by simply moving closer together and then further apart The nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) molecules in the animation are vibrating in this simple mode Molecules with 3 or more atoms can vibrate in more complex patterns A single molecule can vibrate in various ways; This is known as the greenhouse effect (see Figure 1) T2I1_Figure 3gif Figure 3 Total greenhouse gas emissions due to human activities (note that the effects of the different greenhouse gases have been standarised to carbon dioxide equivalents) The inner circle shows greenhouse gas emission shares (in % of total human activityrelated
The main greenhouse gas you should know about is carbon dioxide CO2 is a colorless, nonflammable gas that is both naturally occurring and produced by human industrialization Because CO2 is the GREENHOUSE EFFECT The "greenhouse effect" is the warming that happens when certain gases in Earth's atmosphere trap heat These gases let in light but keep heat from escaping, like the glass walls of a greenhouse First, sunlight shines onto the Earth's surface, where it is absorbed and then radiates back into the atmosphere as heat67 KB Nitrous oxide emissions from agriculture, OWIDsvg 850 × 600;




Greenhouse Gifs Tenor




Top 30 Greenhouse Effect Gifs Find The Best Gif On Gfycat
List Of Greenhouse Gases CO2 from fossil fuel consumption is the best known source of greenhouse gas, though certainly not the only one 11 Water Vapor (H2O) Water vapor, although it sounds innocent enough, is one of the biggest contributors to global climate change Interestingly, water vapor is not directly emitted from human activity The gases that make up Earth's atmosphere are mostly nitrogen and oxygen, and small quantities of trace gases such as argon, neon, helium, the protective ozone layer and various greenhouse gasesGreenhouse gas ý nghĩa, định nghĩa, greenhouse gas là gì 1 a gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2 a gas that causes the Tìm hiểu thêm




Greenhouse Effect Department Of Agriculture Water And The Environment




Via Giphy Global Warming Giphy Earth Gif
Emissions of a broad range of greenhouse gases of varying lifetimes contribute to global climate change Carbon dioxide displays exceptional persistence that renders its warming nearly irreversible for more than 1,000 y Here we show that the warming due to nonCO2 greenhouse gases, although not irreversible, persists notably longer than the anthropogenic changes in the greenhouse gas To prevent the worst effects of climate change, we need to get to zero net greenhouse gas emissions in every sector of the economy within 50 years—and as the IPCC recently found, we need to be on a path to doing it in the next 10 years That means dealing with electricity, and the other 75% too Bill Gates 275M subscribers Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived
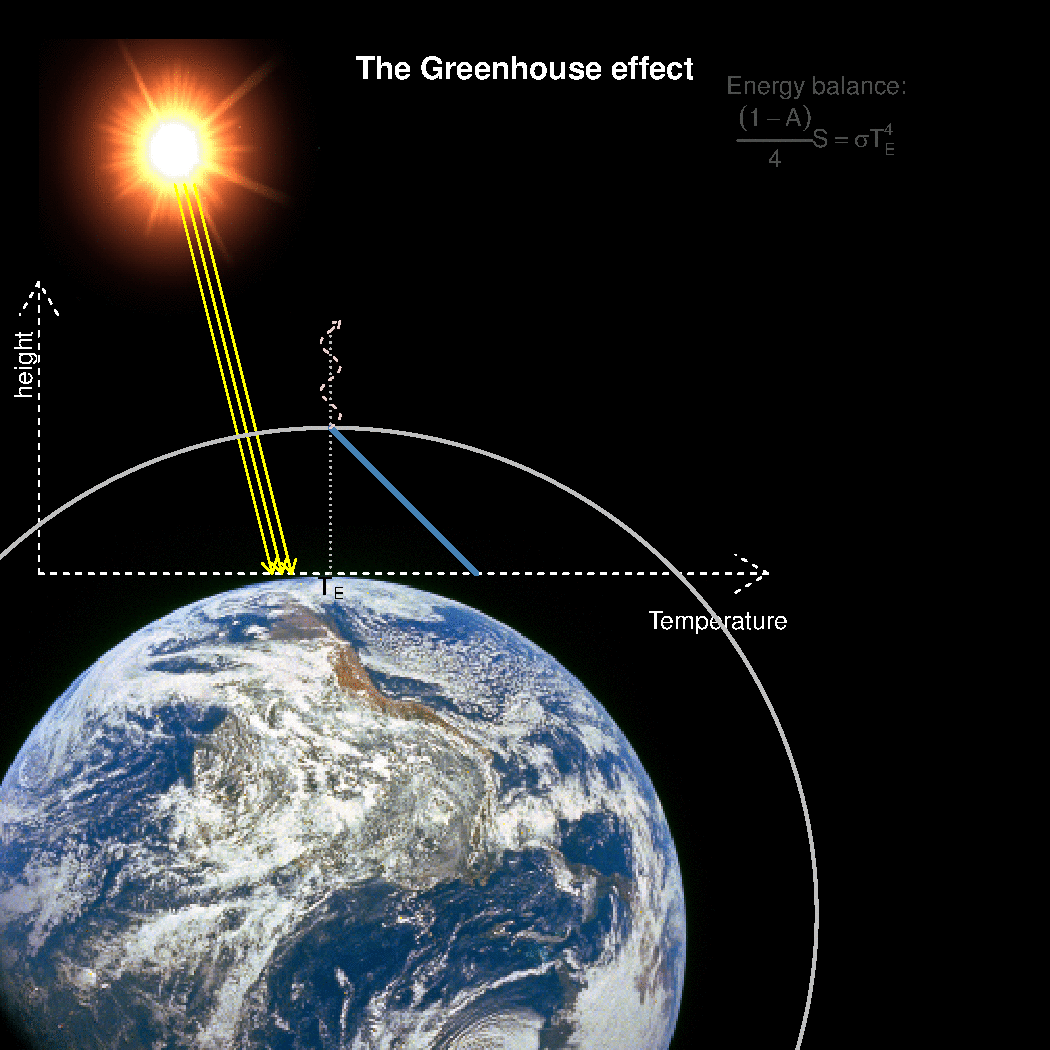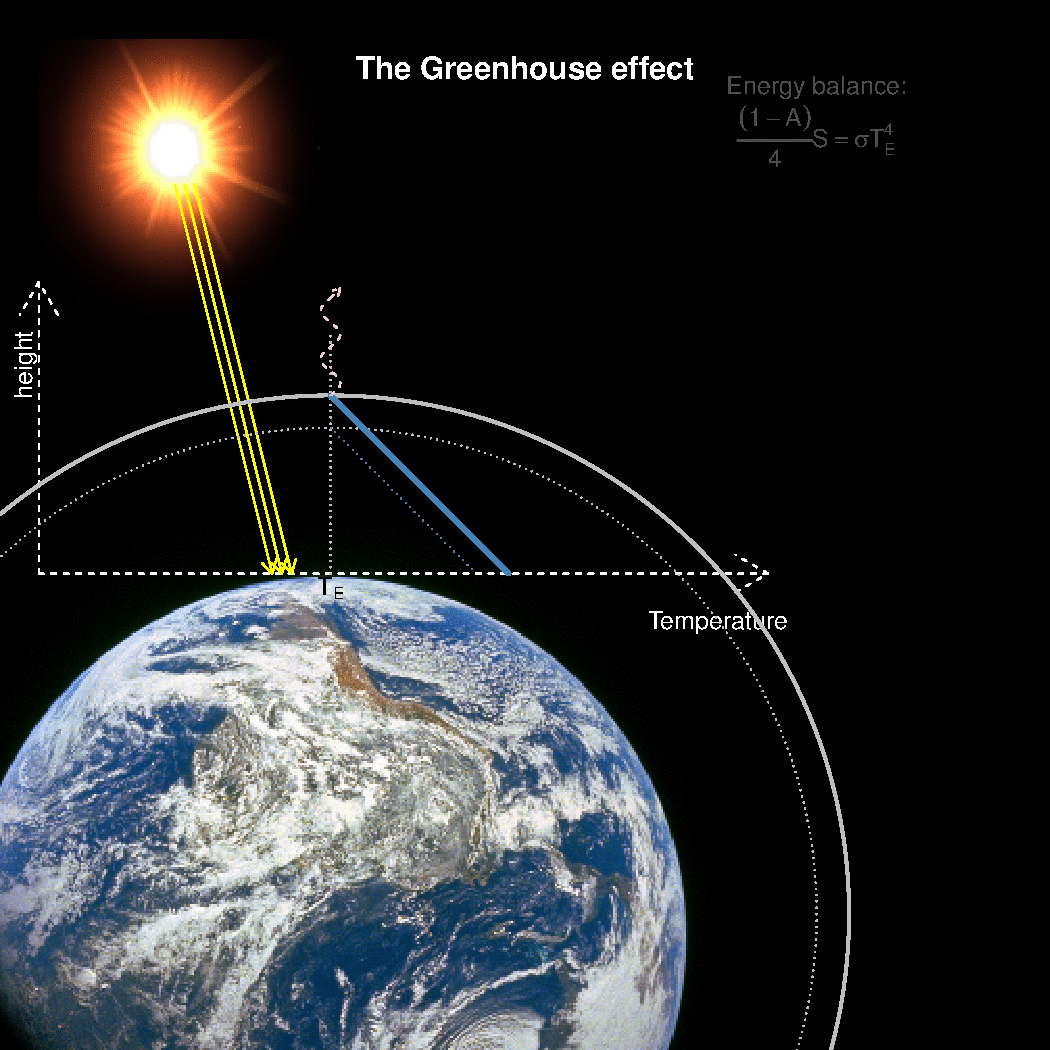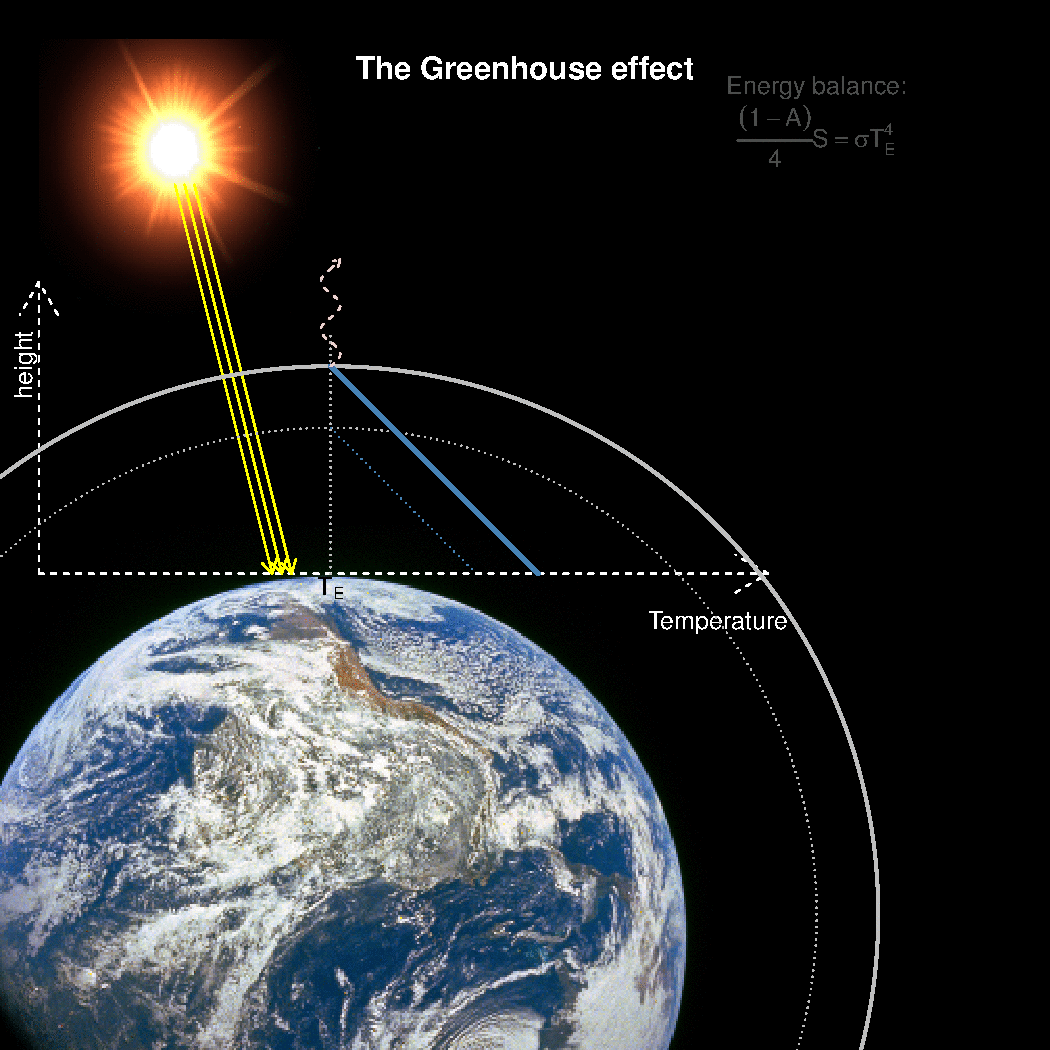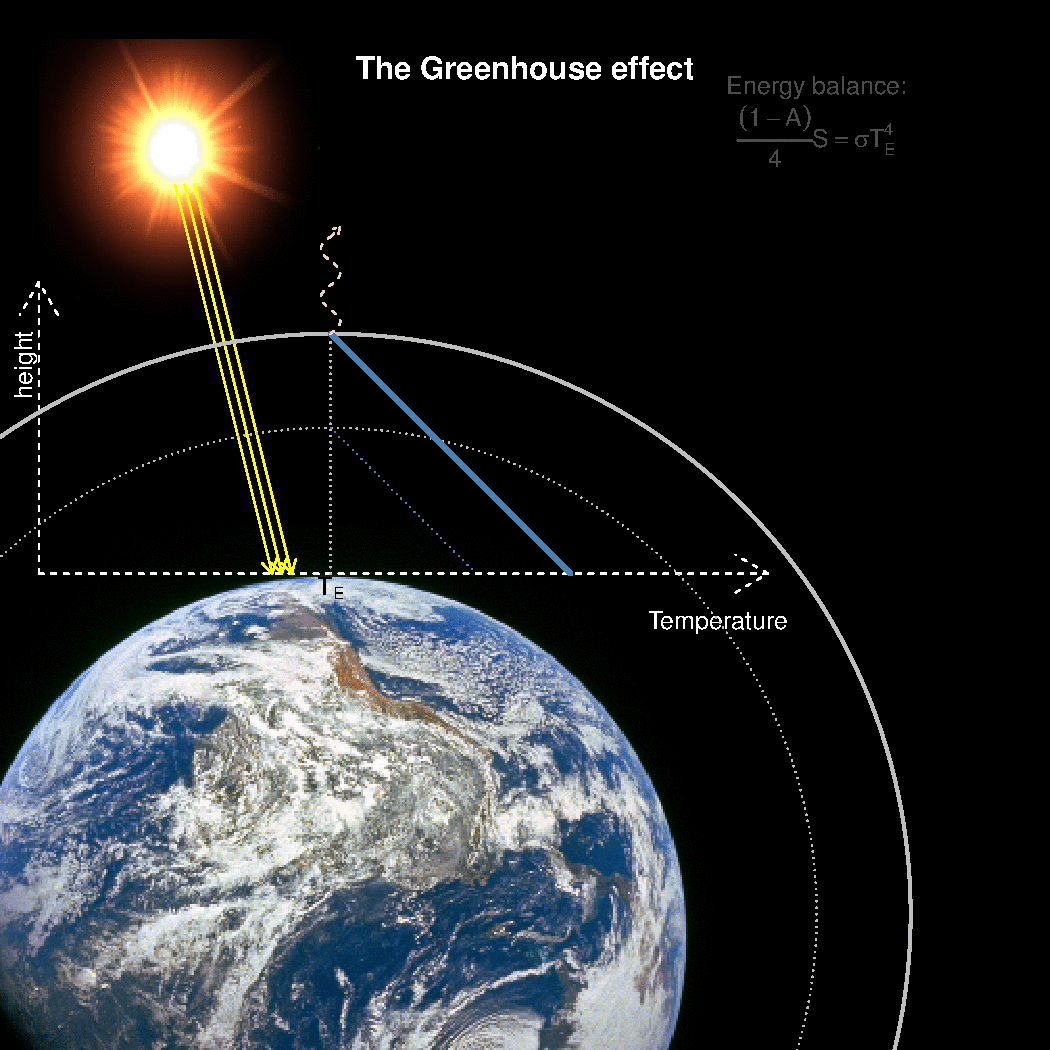



Realclimate What Is The Best Description Of The Greenhouse Effect
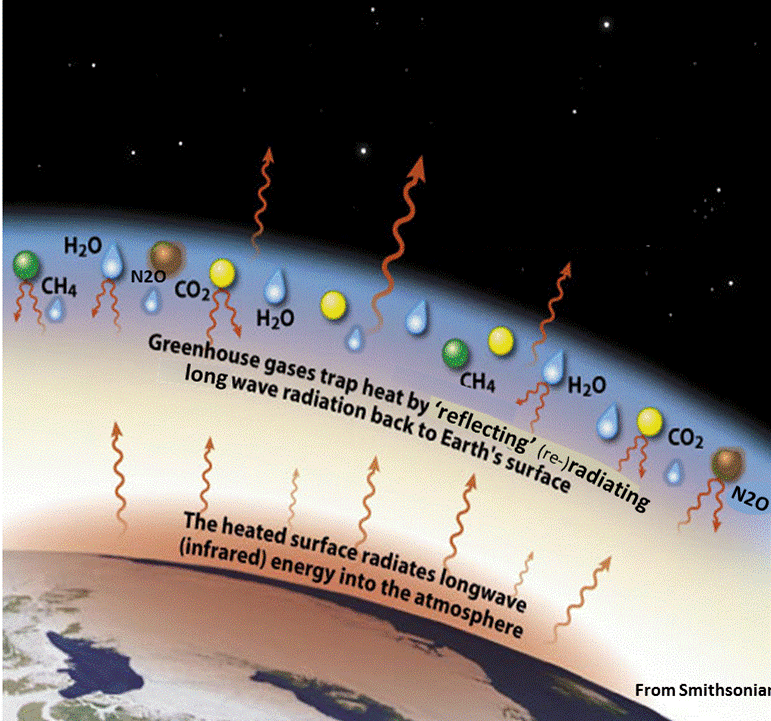



Greenhouse Effect
The answer may not be as clear as one might assume, because the top emitters change depending on how the data is collected and what 3,255 greenhouse gases stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See greenhouse gases stock video clips of 33 sun radiating to a plant thermal radiation effects global warming greenhousegases gases in atmosphere light pollution effect gases cartoon atmosphere gases atmospheric gases cartoon global warmingEach of these different motions is called a




Mr Gruszka S Earth Science Giftionary Day 034 Giftionary Greenhouse Gases



Greenhouse Gases
4B5060 Greenhouse Effect Air vs CO2 Objective To demonstrate the greenhouse effect using an environment of air vs CO 2 and a light source Status Available Assembly Instructions Fill one beaker with CO 2 and keep air in the other Cork both beakers and place a temperature probe in each beaker Set the beakers in front of the light An enhanced greenhouse effect from CO2 has been confirmed by multiple lines of empirical evidence Satellite measurements of infrared spectra over the past 40 years observe less energy escaping to space at the wavelengths associated with CO2 Surface measurements find more downward infrared radiation warming the planet's surface This provides a direct, empirical Smartphones are warming the planet far more than you think Greenhouse gas emissions from computers, phones, and data centers could grow from about 1 percent of global emissions in 07 to over 14 percent in 40 The carbon footprint of smartphones will exceed that of desktop computers, laptops, and displays By Prachi Patel




Challenge 6 Email 14 The Darwin Challenge



Chemistry Greenhouse Carbon Dioxide
The distribution of CH 4 in the atmosphere is affected by sources and sinks at the Earth's surface, chemical loss by reaction with the hydroxyl radical, and by atmospheric transport (principally, winds and convection) Large scale seasonal and spatial patterns in CH 4 distribution can be observed directly from observations at discrete locations, but it is also quite interesting to look at theExternal Geophysics, Climate and Environment Investigating plausible mechanisms to trigger a deglaciation from a hard snowball Earth Guillaume Le Hira,*, Gilles Ramsteina, Yannick Donnadieua, Raymond T Pierrehumbertb a Laboratoire des sciences du climat et de l'environnement (LSCE), CNRS/CEA, baˆt 701, L'Orme des Merisiers, GifsurYvette, FranceThe City of Edinburgh Council July 1 at 736 AM · The draft 30 Climate Strategy recognises that Edinburgh's businesses, communities and people all have an important part to play in helping tackle climate change and invest in a better future Find out more and have your say in the proposals by taking part in the online consultation https




Best Greenhouse Gases Gifs Gfycat




Mr Gruszka S Earth Science Giftionary Day 036 Giftionary Mechanisms Of The Greenhouse Effect
In terms of the net increase in the greenhouse effect due to humanproduced greenhouse gases, CO 2 is responsible for the lion's share CO 2 from fossil fuel burning alone is more than half the net force If you add CO 2 from fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and other minor sources, this comes to a little more than threefourths of the net Now Venus is the poster child for the "runaway greenhouse effect," a testament to the way a planet can change when the cycles that balance its1 greenhouse effect rev gif 768 × 432;676 MB 595pxAtmospheric TransmissionPLpng 595 × 600;97 KB Absorption efficiency graph from Lightning in a Bottlepng 6 × 311;112 KB



c News Sci Tech Climate Disaster Possible By 2100




Greenhouse Gifs Get The Best Gif On Gifer
Black symbols pollution greenhouse gases stock illustrations flying high commercial jet at altitude greenhouse gases stock pictures, royaltyfree photos & images Steam and exhaust rise from different companies on a cold winter day on in Oberhausen, GermanyBrowse greenhouse gas pictures, photos, images, GIFs, and videos on Photobucket Radiative Forcing A simplified animation of Earth's planetary energy balance A planet's energy budget is balanced between incoming (yellow) and outgoing radiation (red);




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Untitled Document
TV Padma looks at how and why greenhouse gas emissions from India are on the rise Greenhouse gas emissions, such as carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide, contribute to global warming and climate change According to the USbased 'think tank' the World Resources Institute, India was responsible for over four per cent of total emissions in 00 — making theGreenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect play an important role in Earth's climate Without greenhouse gases, our planet would be a frozen ball of ice In recent years, however, excess emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases from human activities (mostly burning fossil fuels) have begun to warm Earth's climate at a problematic Each greenhouse gas has a different radiative forcing formula, but the most important is that of CO2 dF = 535 ln (C/C o) Where 'dF' is the radiative forcing in Watts per square meter, 'C' is the concentration of atmospheric CO2, and 'C o' is the reference CO2concentration



1



The Greenhouse Effect
Emission factors for these pollutants for common equipment can be found in Appendix E of the short instructions or Appendix F of the long instructions Reporting these emissions (other than those sources already required to report methane emissions) is completely optional Your help in compiling an accurate greenhouse gas inventory is appreciated65 KB NewZealandgreenhousegasemissionssvg 506 × 354;Causes of global warming The greenhouse effect The average surface temperature of Earth is maintained by a balance of various forms of solar and terrestrial radiation Solar radiation is often called "shortwave" radiation because the frequencies of the radiation are relatively high and the wavelengths relatively short—close to the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum



Ghg Gifs Wifflegif



Graphic The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
For the second time in just a few weeks, the city and state have gone to federal court in an effort to defend federal rules intended to limit emissions of climatechanging greenhouse gasesA greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3)Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gases




Global Warming Some Facts And Figures Album On Imgur
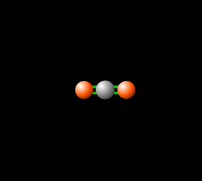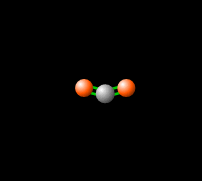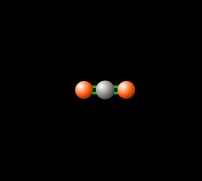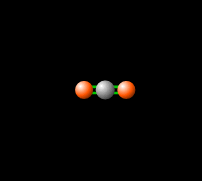



Greenhouse Gas Energy Education
Since the Industrial Revolution, rising emissions of greenhouse gases—including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and others—have been the driving force behind climate change Who is responsible for emitting the most greenhouse gases?The Yedoma layer, a permafrost layer containing a massive amount of underground ice in the Arctic regions, is reported to be rapidly thawing In this study, we develop the Permafrost Degradation and Greenhouse gasses Emission Model (PDGEM), which describes the thawing of the Arctic permafrost including the Yedoma layer due to climate change and the greenhouse gas (GHG)Greenhouse gas (GHG) metrics, that is, conversion factors to evaluate the emissions of nonCO2 GHGs on a common scale with CO2, serve crucial functions in the implementation of the Paris Agreement While different metrics have been proposed, their economic costeffectiveness has not been investigated under a range of pathways, including those substantially overshooting the




The Greenhouse Effect Gif Gfycat



Greenhouse Gases Gifs Get The Best Gif On Giphy
Greenhouse ý nghĩa, định nghĩa, greenhouse là gì 1 a building with a roof and sides made of glass, used for growing plants that need warmth and Tìm hiểu thêm A new way of comparing greenhouse gases could help us meet Paris Agreement goals According to the Paris Agreement, the world needs to limit global warming to well below 2°C and to strive towardGrasslands absorb and release carbon dioxide (CO 2), emit methane (CH 4) from grazing livestock, and emit nitrous oxide (N 2 O) from soils Little is known about how the fluxes of these three greenhouse gases, from managed and natural grasslands worldwide, have contributed to past climate change, or the roles of managed pastures versus natural grasslands




This Viral Climate Gif Offers An Incredibly Clear View Of Rising Temperatures Vox
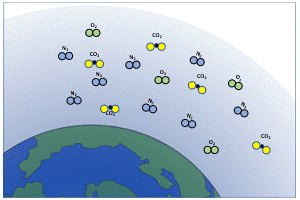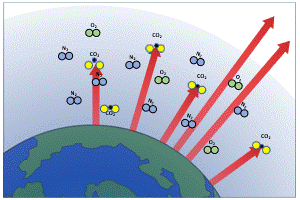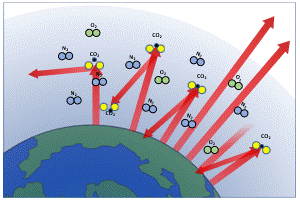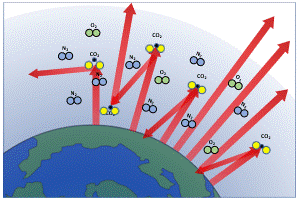



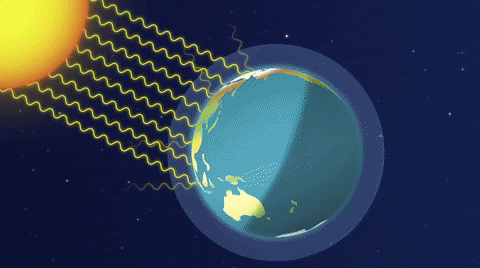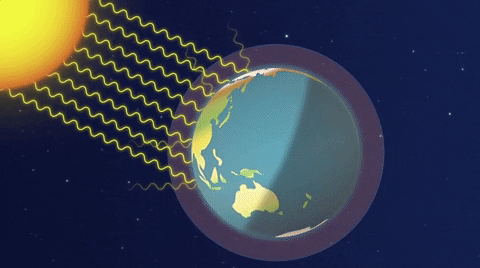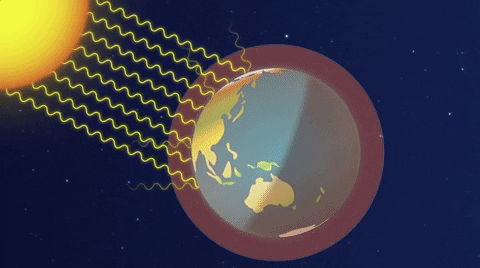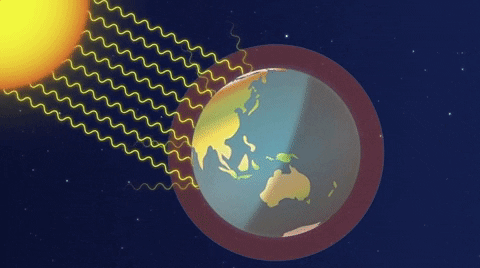
Understanding The Greenhouse Effect Changing Climate Our Future Our Choice Museum Of The Earth
This study filters out variations in Earth's energy In terms of greenhouse gas emissions, this means that hybrid cars on average produce 035 fewer pounds of greenhouse gas per mile than regular cars, adding up to a tremendous environmental advantage over the course of the car's lifespan However, this only remains true for hybrid vehicles that charge their batteries themselves The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,




How Do Greenhouse Gases Actually Work On Make A Gif




Report Trump S Public Lands Attacks Have Huge Climate Change Impact The Wilderness Society



Georgia Natural Gas Atlanta Natural Gas Company




File Greenhouse Gases In Global Warming Effect Gif Wikimedia Commons
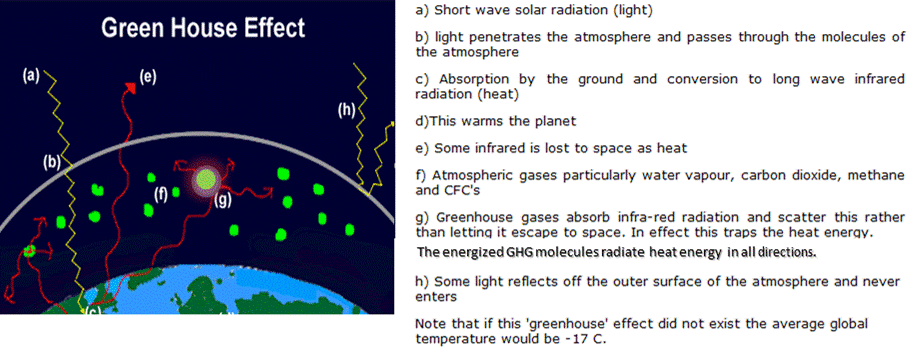



Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Gases




Esa Space For Kids Greenhouse Gases Star In Space Movies
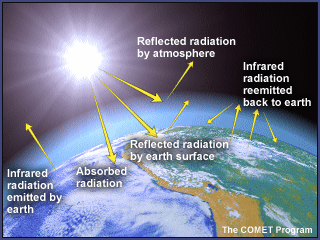



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




Best Greenhouse Gas Gifs Gfycat




Best Greenhouse Gases Gifs Gfycat




Trump Unveils Plan To Weaken Greenhouse Gas Limits On Power Plants
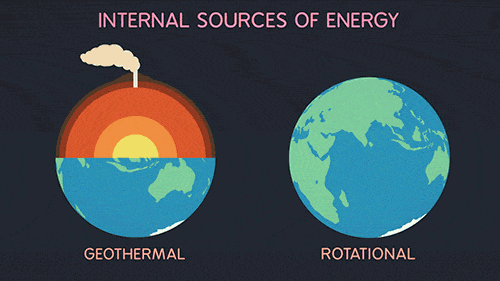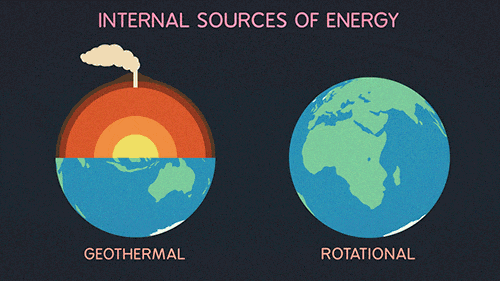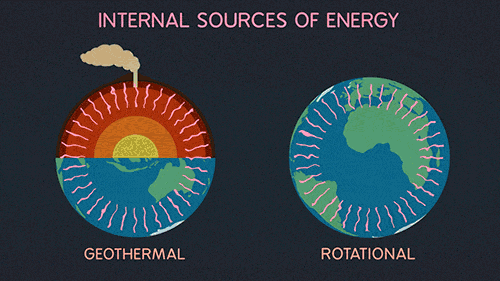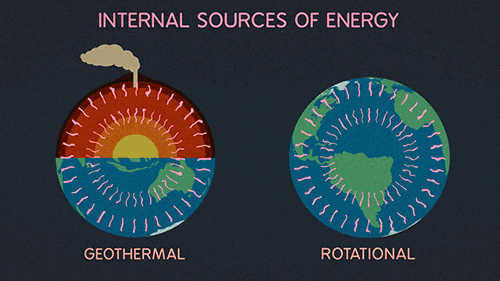



Global Warming And The Greenhouse Gases Science Amino




Best Greenhouse Gases Gifs Gfycat




Hydrosphere Gifs Get The Best Gif On Gifer




Best Greenhouse Gases Gifs Gfycat




Global Warning Global Warming O Level Chemistry Notes




What Climate Change Looks Like In 6 Gifs Planet Aid Inc




Global Greenhouse



Greenhouse Gases Gif




Smartphones Are Warming The Planet Far More Than You Think



Another Year Another Record High For Greenhouse Gases Climate Central




Climate Change In W Va Destruction Disease And Deception The Basics Of Global Warming Wboy Com




What Climate Change Looks Like In 6 Gifs Planet Aid Inc




Global Warming Pollution Awareness




Mr Gruszka S Earth Science Giftionary Day 036 Giftionary Mechanisms Of The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gasses Gif Annasaraclasine




Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country Between 1850 16




Eo Topics Satellite Missions Eoportal Directory




Greenhouse Gases Gif 5 Gif Images Download




Carbon Dioxide Absorbs And Re Emits Infrared Radiation Ucar Center For Science Education



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau
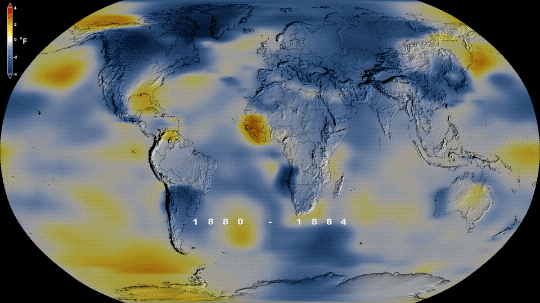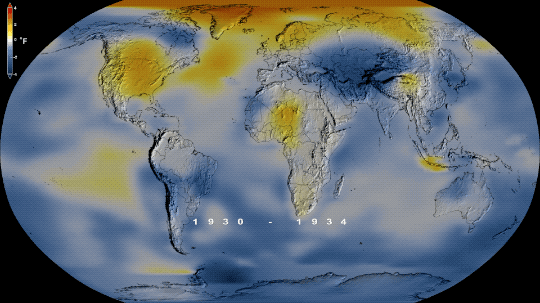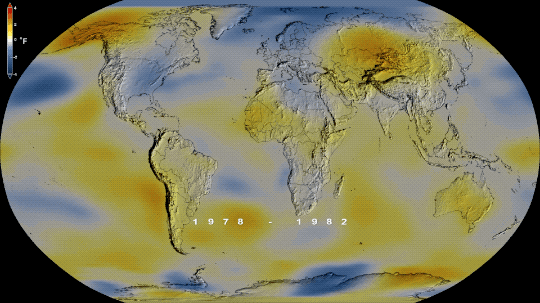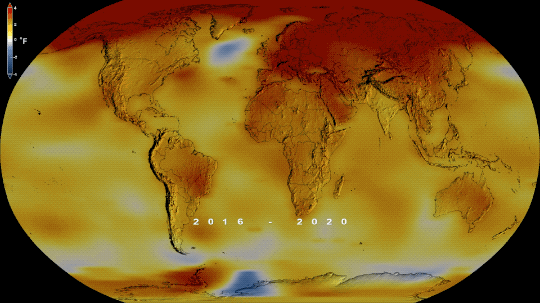



Tumblr



Climate And Greenhouse Gasses Science News




Greenhouse Effect For Kids On Make A Gif
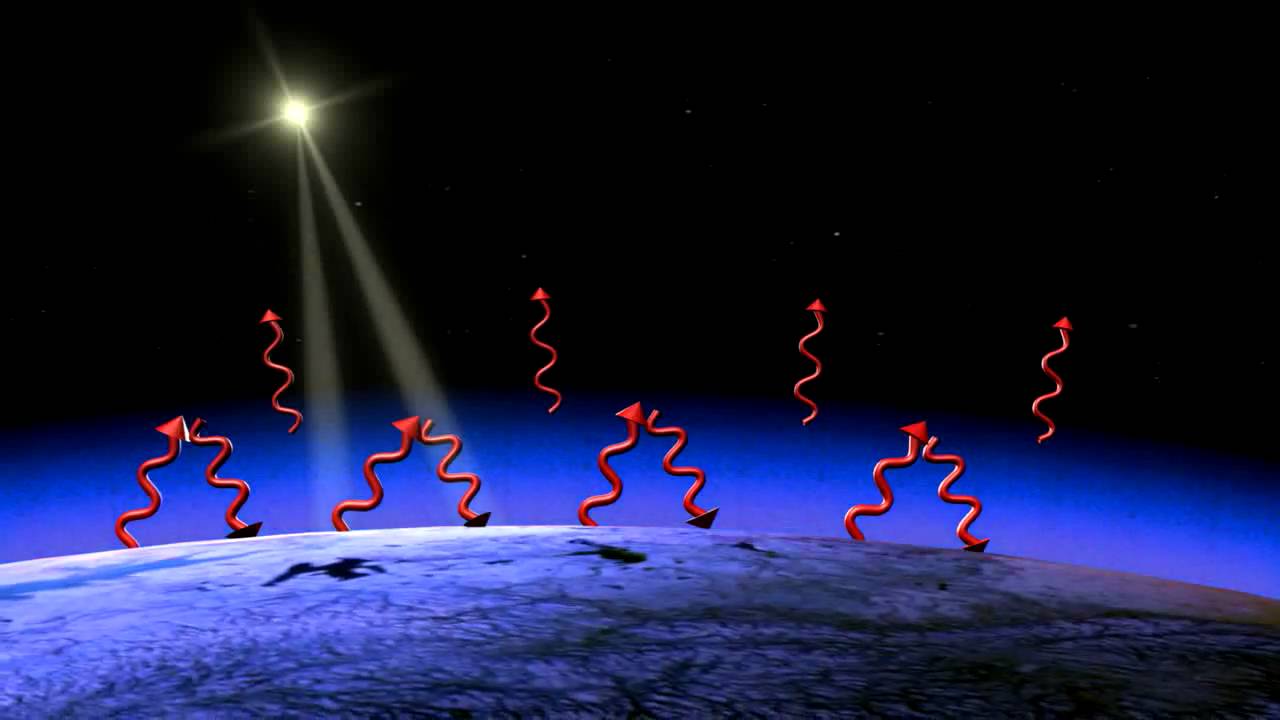



Greenhouse Gases Animation 7p Youtube
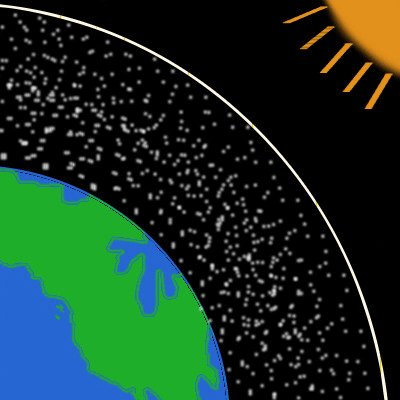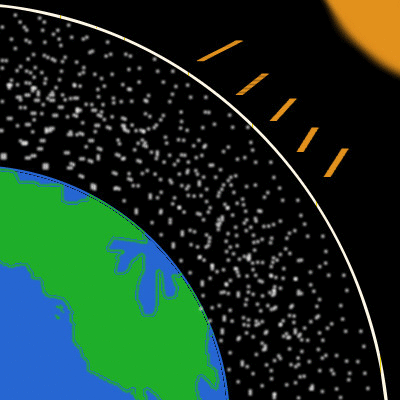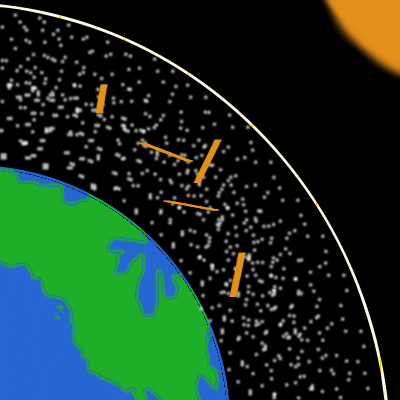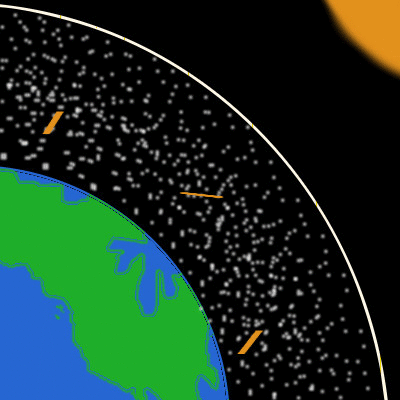



A Discussion About Climate Change Part 2 Atmosphere Steemit



Q Tbn And9gctkbbp5kfy Zbjp6l9wtd5beerxr5pe0s5s4ourd 4uq64ft6ru Usqp Cau




Best Greenhouse Gases Gifs Gfycat
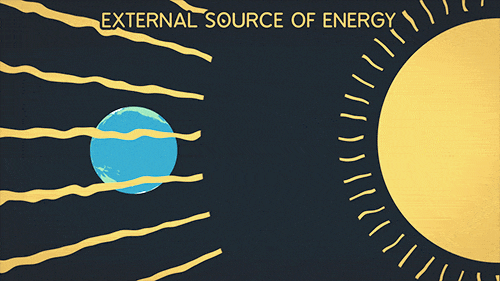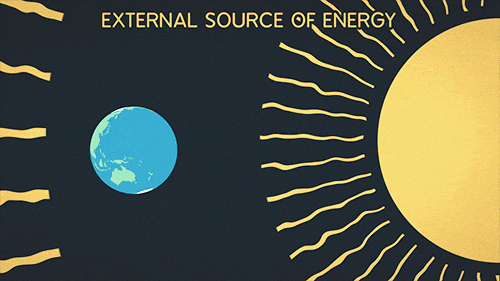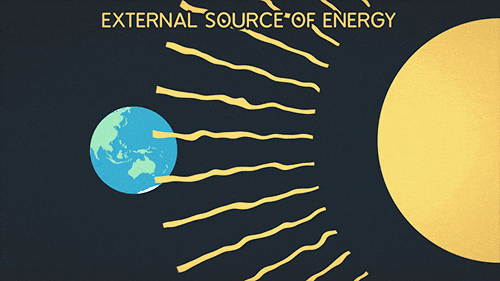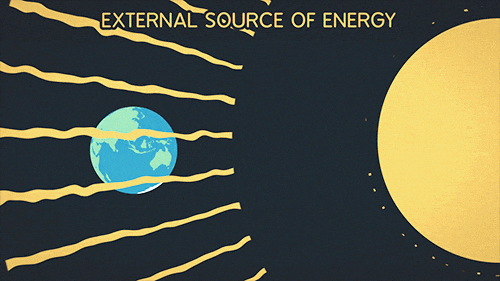



Greenhouse Gifs Get The Best Gif On Gifer




How Greenhouse Gas Works Desktop Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases Art Dolls




Aluminium For Future Generations Greenhouse Gases



Blog Posts Science News




Best Greenhouse Gases Gifs Gfycat
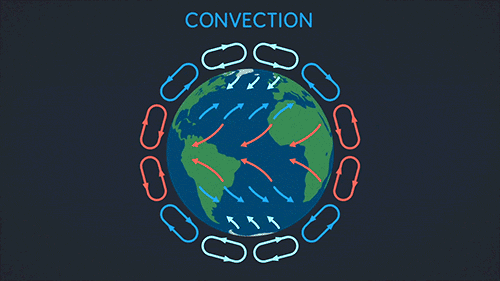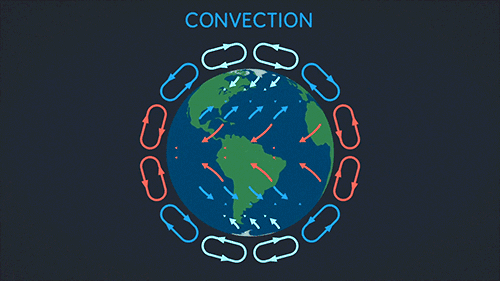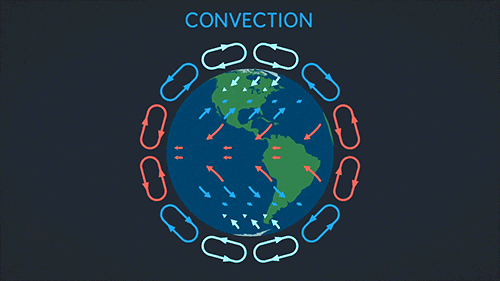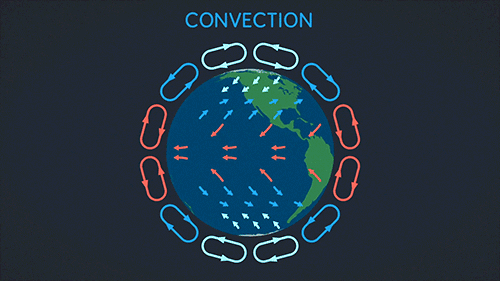



Earth Science The Sun Biosphere Gif On Gifer By Mosius



3




최고 Greenhouse Gases Gif들 Gfycat




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
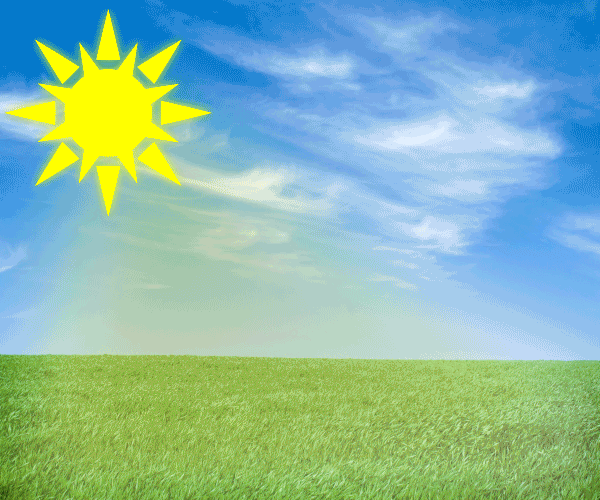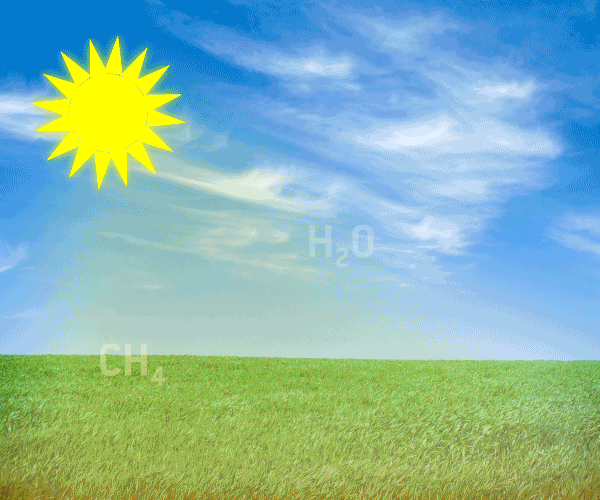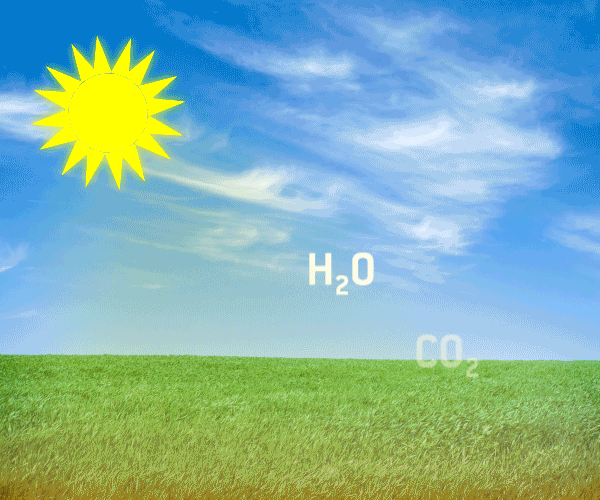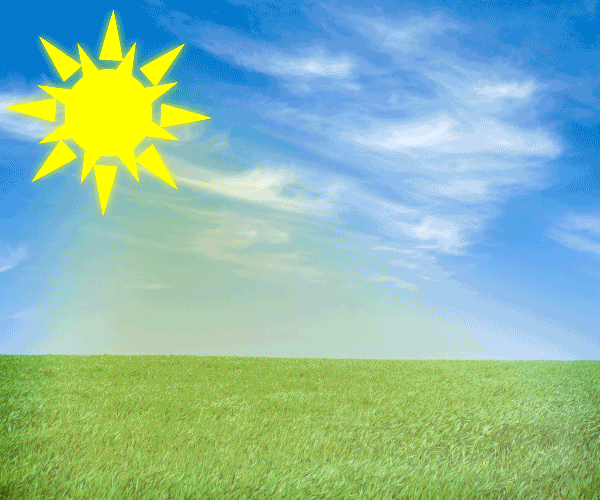



1 2 The Greenhouse Gases Ghg A Greener Future




Best Greenhouse Gases Gifs Gfycat




Mr Gruszka S Earth Science Giftionary Day 034 Giftionary Greenhouse Gases




To Fight Climate Change Convert One Greenhouse Gas Into Another




What Climate Change Looks Like In 6 Gifs Planet Aid Inc




Greenhouse Gas Gifs Get The Best Gif On Giphy




Gas Emission Gifs Get The Best Gif On Giphy
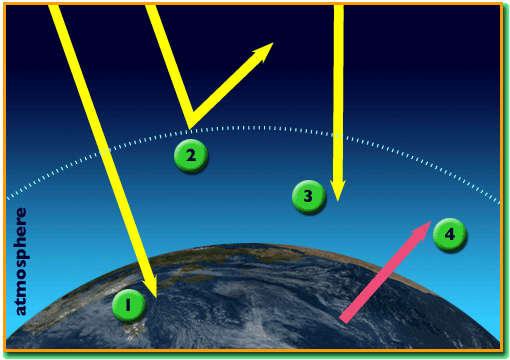



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Amnh




Methan Gifs Get The Best Gif On Giphy



Good Greenhouse Gases Science News




Mr Gruszka S Earth Science Giftionary Day 034 Giftionary Greenhouse Gases




Satellites Providing Clear Picture Of Greenhouse Gases




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Ideas On Make A Gif
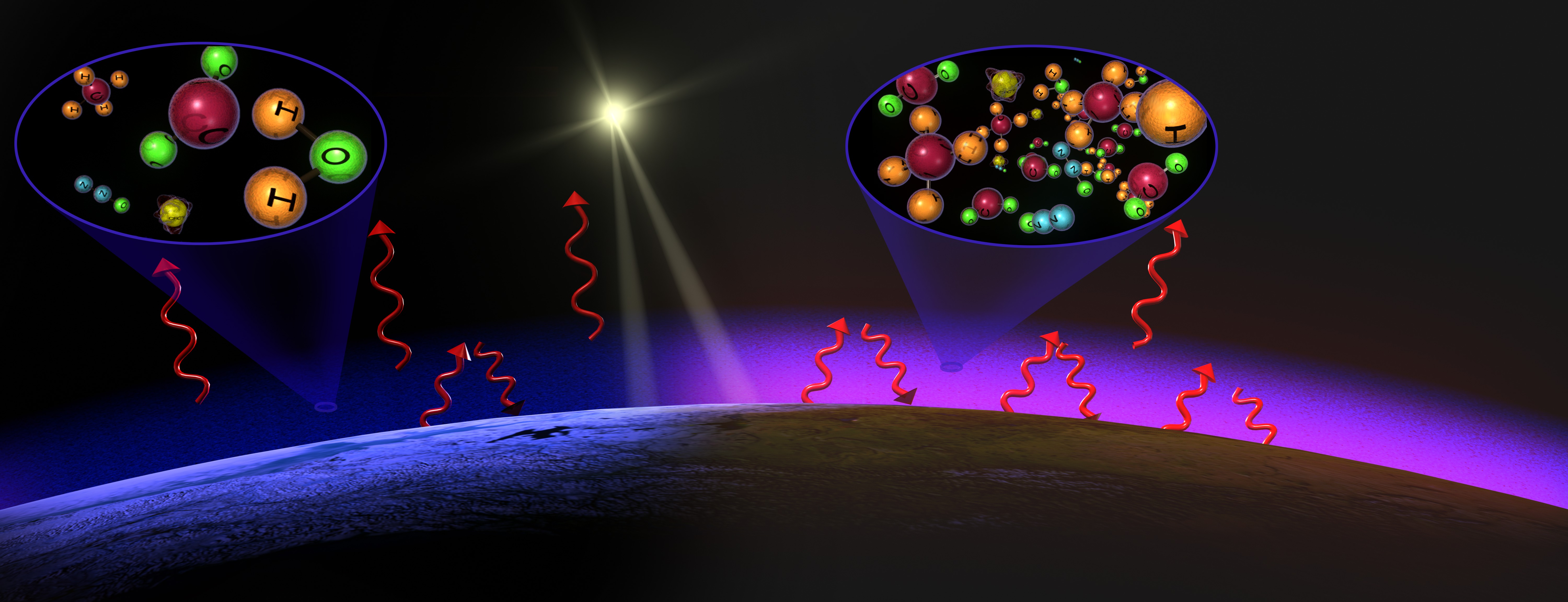



Cilab Greenhouse Gases Effect On Global Warming
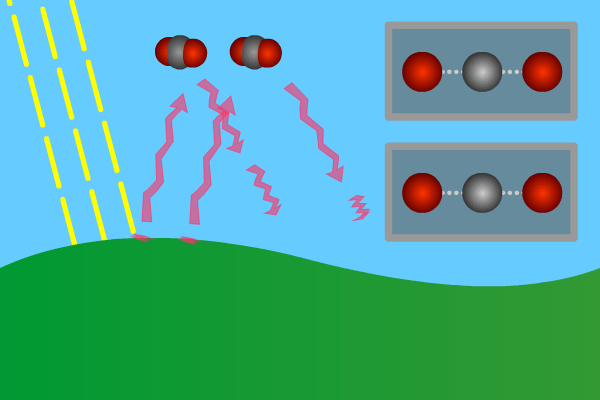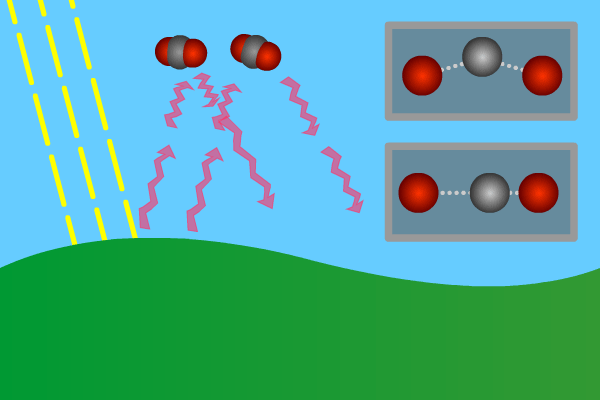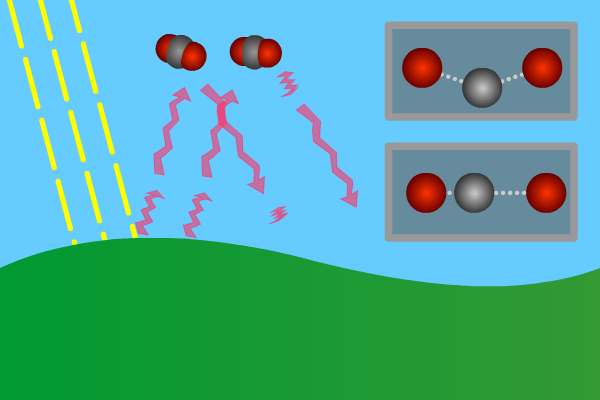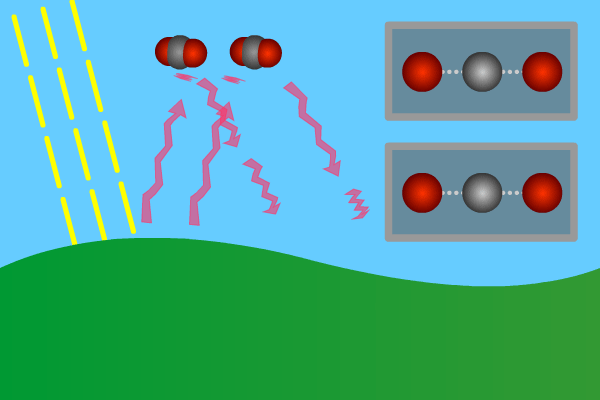



1 The Natural Greenhouse Effect
.gif)



Greenhouse Gases And The Infrared Gas Analyzer
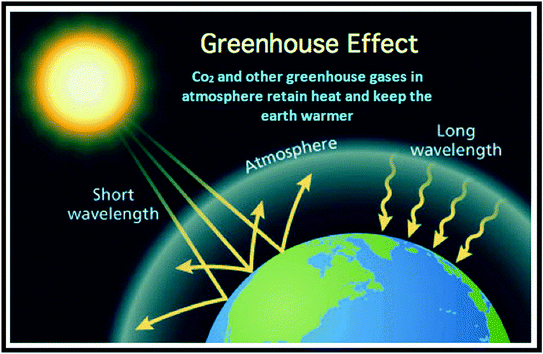



Reducing The Impacts Of Greenhouse Gases Springerlink




Futurama Global Warming Youtube




Greenhouse Gases Ayy Gif Find On Gifer
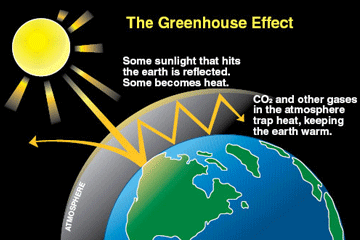



How Do Greenhouse Gases Affect The Environment Socratic



Chemistry Greenhouse Carbon Dioxide



Greenhouse Gases




How Do Greenhouse Gases Actually Work On Make A Gif




Greenhouses Gifs Get The Best Gif On Giphy



Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Download Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Png Images Free Cliparts On Clipart Library



Chemistry Greenhouse Carbon Dioxide
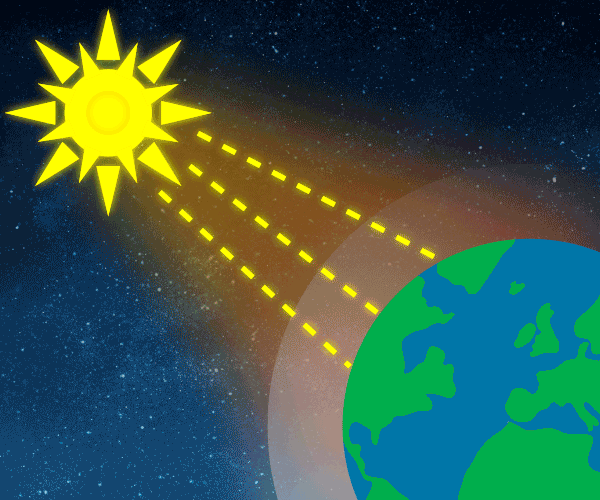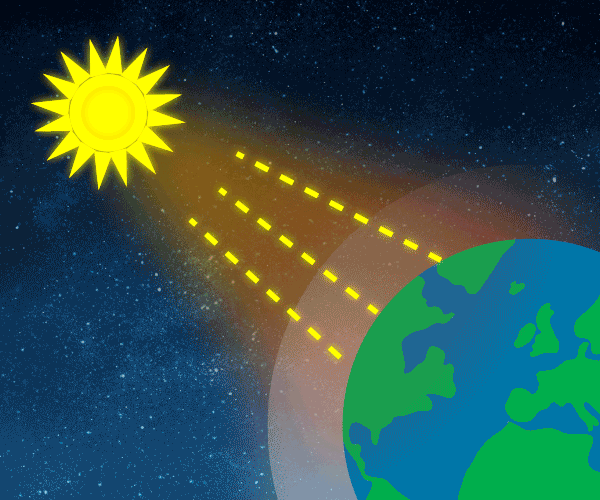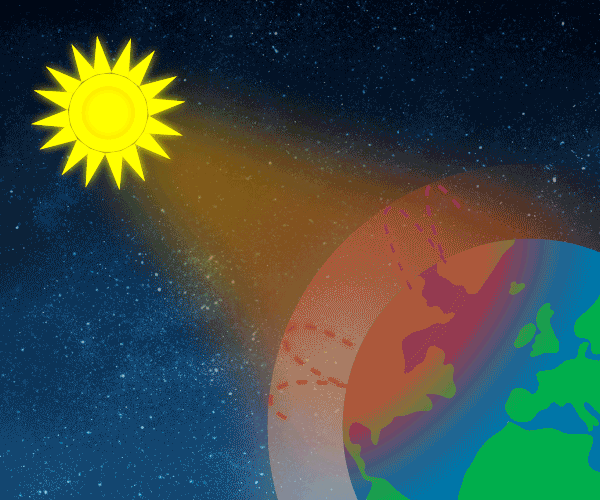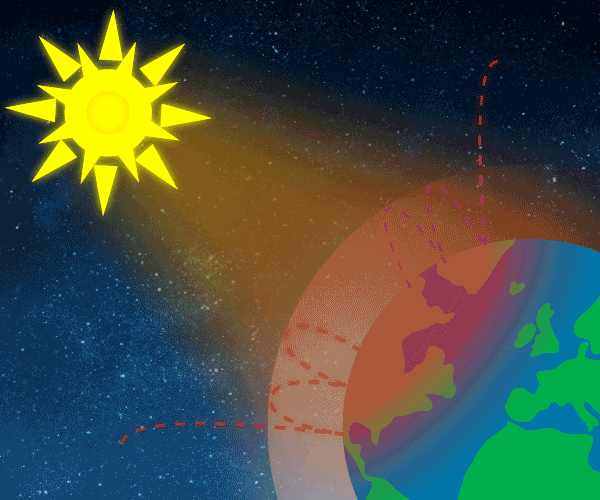



Climate Change Is Real Green House Gases Are The Cause And Humans Contribute
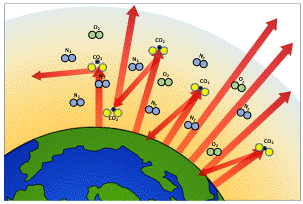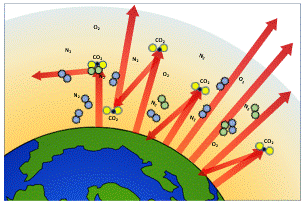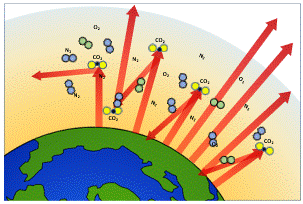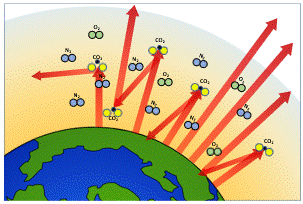



Understanding The Greenhouse Effect Changing Climate Our Future Our Choice Museum Of The Earth




1 The Natural Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Green House Effect Greenhouse



Greenhouse Effect Gifs Get The Best Gif On Giphy


